New highlight shows how changes in METTL3 localisation could hold the key to new antiviral strategies against SARS-CoV-2.
June 1, 2023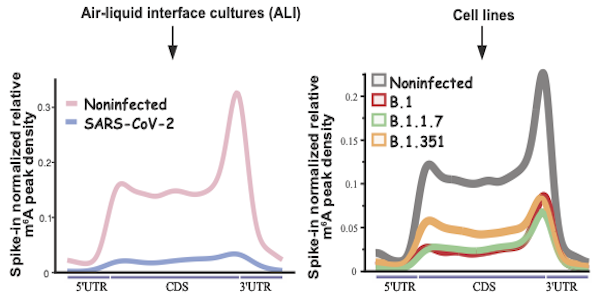
We have published a new data highlight, entitled: METTL3 localisation during SARS-CoV-2 infection could highlight new novel antiviral strategy, which is based on Vaid and Mendez et al. (2023).
The recent COVID-19 pandemic has highlighted the importance of finding novel routes for treatment in minimising the negative effect of infectious diseases on society. The N6-Methyladenosine modification (m6A) is one of the most common cellular RNA modifications, and known to play a crucial role in the regulation of RNA metabolism during the stress response. Vaid and Mendez et al investigated changes in m6A expression during SARS-CoV-2 infection to determine whether this could be the key to novel or improved antiviral therapeutics for SARS-CoV-2. They found that SARS-CoV-2 infection caused a loss of m6A in cellular RNAs. This was related to partial relocalisation of the methyltransferase METTL3/METTL14 complex from the nucleus to the cytoplasm. Both sequencing data and analysis code from this study are shared.
Read more in the Data Highlight: METTL3 localisation during SARS-CoV-2 infection could highlight new novel antiviral strategy. You’ll also see other highlights on related topics at the bottom of the article.
Do you have some data-driven life science research that you’d like to highlight, or even present as a service, on the SciLifeLab Data Platform? If so, please fill out the forms on the appropriate pages or get in touch with us.