Glossary
- FAIR Principles
- FAIR is a framework designed to enhance the Findability, Accessibility, Interoperability, and Reusability of digital objects, comprising 15 guiding principles that ensure data and metadata are effectively managed and shared. It prioritises machine-actionability, ensuring that computational systems can efficiently find, access, interoperate, and reuse data with minimal human intervention. A key aspect of FAIR is the use of persistent identifiers (e.g., ORCID iDs, DOIs, RORs, RRIDs, RAiDs). High-quality metadata is essential in this framework, providing rich contextual information that enables accurate data discovery, integration, and reuse. The FAIR principles emphasise that data and metadata should be well-structured, openly accessible where possible, and supported by standardised formats and vocabularies to maximise interoperability and reusability. By implementing these principles, FAIR enables seamless data sharing and integration, supporting the computational nature of modern research.
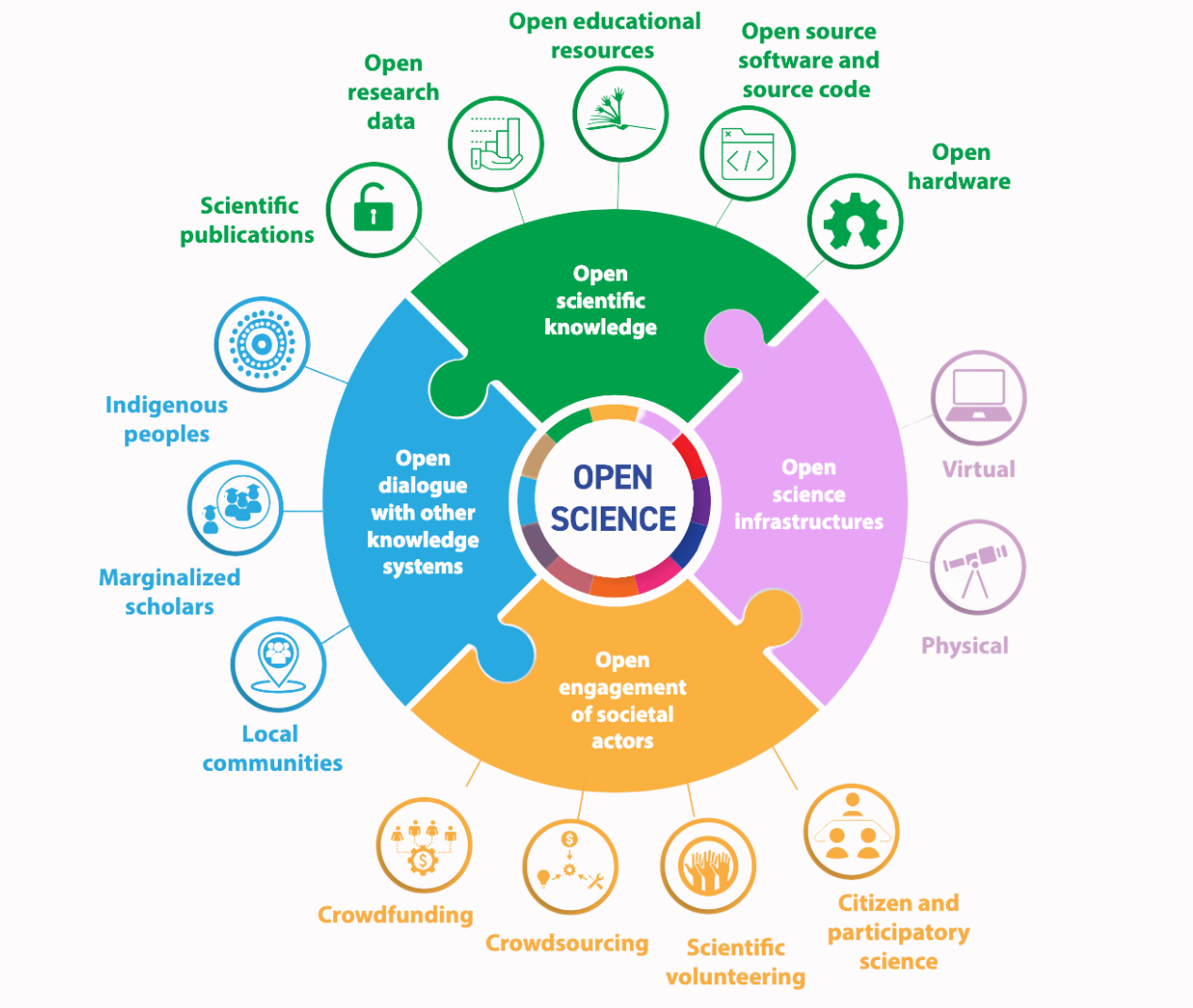
- UNESCO Open Science Definition
- An inclusive construct that combines various movements and practices aiming to make multilingual scientific knowledge openly available, accessible and reusable for everyone, to increase scientific collaborations and sharing of information for the benefits of science and society, and to open the processes of scientific knowledge creation, evaluation and communication to societal actors beyond the traditional scientific community.