FunCoup 6: Large-scale functional association networks with regulatory links and integrated tools
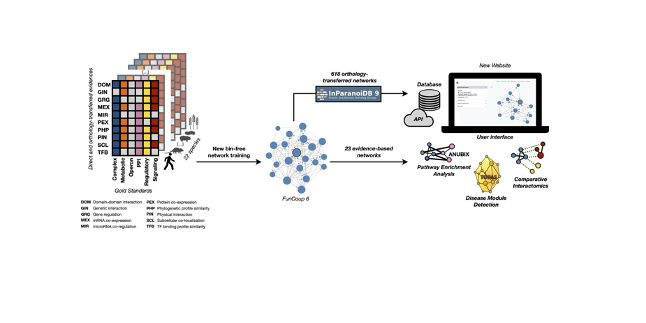
This highlight features the new update to the FunCoup database, which provides a global, species‑spanning view of functional coupling among genes and proteins. In this release, FunCoup 6 greatly expands gene regulatory links and species, as well as offering an improved user interface and new analytical tools.
The article “FunCoup 6: advancing functional association networks across species with directed links and improved user experience”, published in Nucleic Acids Research (2025), presents a major upgrade.
It includes the following key innovations: Extension of network coverage through bin‑free Bayesian training across 23 primary species, plus network generation for an additional 618 species. Expanded regulatory link coverage: FunCoup 6 now includes over half a million directed gene regulatory links in the human network alone. 13 species in FunCoup now contain regulatory links. Inclusion of pathway enrichment tools (ANUBIX, EASE) and a new module for disease or drug target module detection using the TOPAS algorithm. A redesigned website and updated API to facilitate user access and integrative analyses. A new mode of ‘comparative interactomics’ for exploring network conservation in multiple species by ortholog‑alignment. FunCoup 6 is also available as a Cytoscape app
This resource strongly aligns with the goals of the functional genomics research by enabling integrative views of functional coupling and regulatory interactions across species. The regulatory links and module detection facilitate deeper hypotheses about pathogen‑host interactions, drug targets, and conserved pathways across species, relevant to pandemic preparedness and translational biology.
Article
DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkae1021
Buzzao, D., Persson, E., Guala, D., & Sonnhammer, E. L. (2025). FunCoup 6: advancing functional association networks across species with directed links and improved user experience. Nucleic Acids Research, 53(D1), D658-D671.
Funders
Swedish Research Council [2019–04095]. Open access funding is provided by Stockholm University.